Describe Two Ways in Which Antibiotic Resistance Can Become Widespread
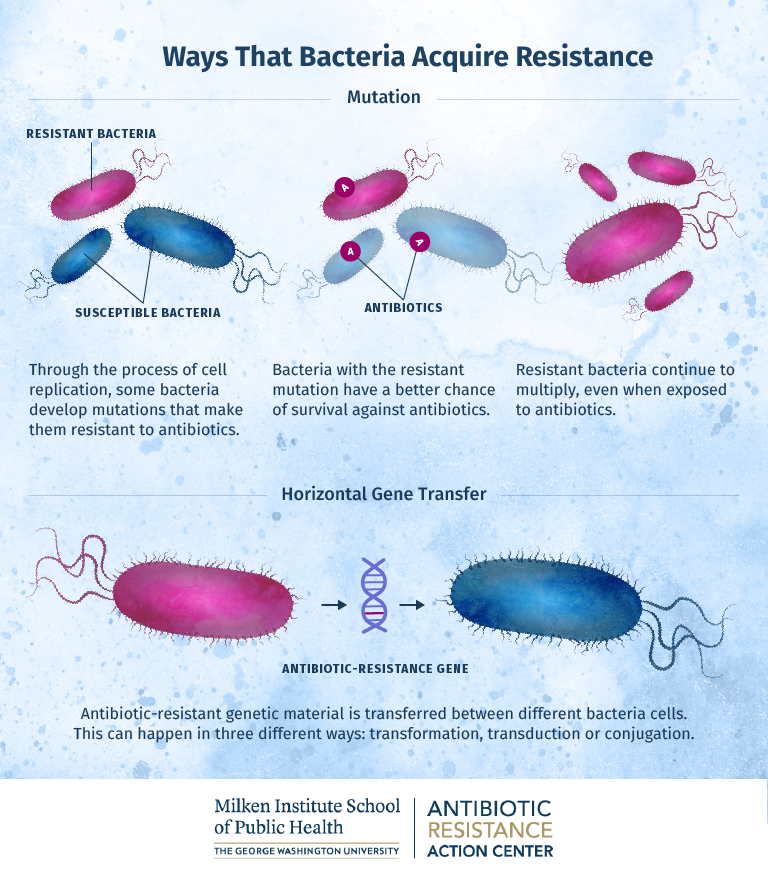
This would give us more medical weapons to fight bacteria and reduce the chances that antibiotic resistance would turn into a widespread problem. There are two main ways that bacterial cells can acquire antibiotic resistance.
How Bacteria Build Resistance At The Cellular Level Online Public Health
Bacteria and fungi can carry genes for many types of resistance.
. Bacteria can produce pumps that sit in their membrane or cell wall. This means better prescription practices by doctors and wiser use by patients. This is why some antibiotics are not expected to work on certain types of infections.
Failing to complete the fully prescribed course by a doctor. Mechanical barrier altering the required intracellular dose of antibiotic. Cell entry - many antibiotics need to enter bacteria to kill them.
A _____ b _____. Efflux pumps bacteria can use these to pump antibiotics out of themselves before the drugs have had a chance to work. Prevention and control.
Enzymatic barrier expression of a detoxifying enzyme that modifymodifies the antibiotic. Gene transfer- bacteria swap pieces of DNA with other bacteria via pili or plius. This allows the bacteria to adapt to the antibiotic because the incomplete treatment did not kill the bacteria.
Check your local farmers markets and food co-ops for the best deals on organic milk and meat. Target protection barrier mutation or expression of a molecule impairing the antibiotic recognition and activity. This form of horizontal gene transfer HGT enables antibiotic resistance to be transferred among different species of bacteria.
This renders the drugs useless against the new resistant strains allowing resistance to grow and spread to other germs creating drug-resistant infections that can be difficult to treat. During transformation - in this process akin to bacterial sex microbes can join together and transfer DNA to each other. But antibiotic-resistant germs find ways to survive.
To survive germs develop defense strategies against antibiotics called resistance mechanisms. Some resistant germs can also give their resistance directly to other germs. They use special holes on the bacterias surface to do this but bacteria can close these holes or get rid of them completely.
The other way that bacteria acquire resistance is through horizontal gene transfer. Absence of new antibiotics being discovered. If we have a broader range of antibiotics that work in different ways we can reduce our reliance on a few specific antibiotics.
Describe two ways a population of bacteria can acquire antibiotic resistance 1. Vaccines have also been developed that can prevent bacterial infection. Examples of bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics include methicillin-resistant.
Two years ago this essentially happened when member states of the WHO agreed to accept a Global Action Plan by then antibiotic resistance was a problem that had already been on the radar for. Use of antibiotics in farming. On a small circular extrachromosomal piece of DNA called a plasmid - one plasmid can encode resistance to many different antibiotics.
Some make people crops or. Another way in which bacteria are becoming resistant to antibiotics is the. Patients not finishing the entire antibiotic course.
Antibiotic resistance loss of susceptibility of bacteria to the killing bacteriocidal or growth-inhibiting bacteriostatic properties of an antibiotic agent. How is antibiotic resistance becoming such a widespread phenomenon. In summary the 6 main causes of antibiotic resistance have been linked to.
Different selective pressures may lead to mutations that coincidentally confer a level of antibiotic resistance. Antibiotics kill germs that cause infections. Growing human and animal populations along with increasing international trade and travel have accelerated the transfer and spread of resistant strains of bacteria turning them into a.
Mutation- mistakes during DNA replication produces new alleles 2. Describe two ways in which antibiotic resistance can become widespread. These so-called efflux pumps are very common in bacteria and can transport a variety of compounds such as signal molecules and nutrients.
Our over-use and misuse of antibiotics in humans animals and agriculture has led to the widespread rise of antibiotic resistance. A simple technical definition of the various resistance mechanisms may be proposed for classification. What doctors and pharmacists can.
When a resistant strain of bacteria is the dominant strain in an infection the infection may be untreatable and life-threatening. Poor infection control in health care settings. Pump the antibiotic out from the bacterial cell.
Mutations in ribosomal protein genes leading to antibiotic resistance have a number of extraribosomal effects mistranslation temperature sensitivity phage propagation etc that influence cell function. Stop the antibiotic from reaching its target. The CDC describes how animals raised in concentrated animal feed lots CAFOs are contributing to the antibiotic-resistance problem.
Antibiotic resistance is accelerated by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics as well as poor infection prevention and control. In livestock food hospitals and the community at large. Find step-by-step Biology solutions and your answer to the following textbook question.
Spread of Germs Resistance Mechanisms. Overuse of antibiotics in livestock and fish farming. DNA tells the germ how to make specific proteins which determine the germs resistance mechanisms.
And even when new antibiotics become available theyll still face the problem of evolving drug resistance. Poor hygiene and sanitation. Antibiotic-resistant germs can multiply.
How Antibiotic Resistance Spreads 1 Germs bacteria and fungi are everywhere. With antibiotics so likely to meet eventual resistance the best tool we currently have is stronger antibiotic stewardship. One is through mutations that occur in the DNA of the cell during replication.
The trend of using antibiotics in feed has increased with the greater numbers of animals held in confinement. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria develop defenses against the antibiotics designed to kill them. Dont eat dairy products and meats that were exposed to antibiotics.
These can lead to the effectiveness of antibiotics being reduced and the. Steps can be taken at all levels of society to reduce the impact and limit the spread of resistance. However bacteria can also acquire genes that allow them to become resistant to.
The antibiotics in the feed of some nonorganic farm animals may contribute to antibiotic resistance. This innate resistance is naturally part of the bacteria genetic make-up or part of the DNA. People contribute to antibiotic resistance by not completing their full course of antibiotics as prescribed by doctors when they are sick.
There are a number of ways to get a resistance gene. Horizontal gene transfer HGT Bacteria are very good at sharing genes including genes for antibiotic resistance.

Antibiotic Resistance How To Prevent The Next Public Health Emergency Mit Department Of Biology

Infographic About The Mechanisms Of Antibiotic Resistance In Bacteria Download Scientific Diagram

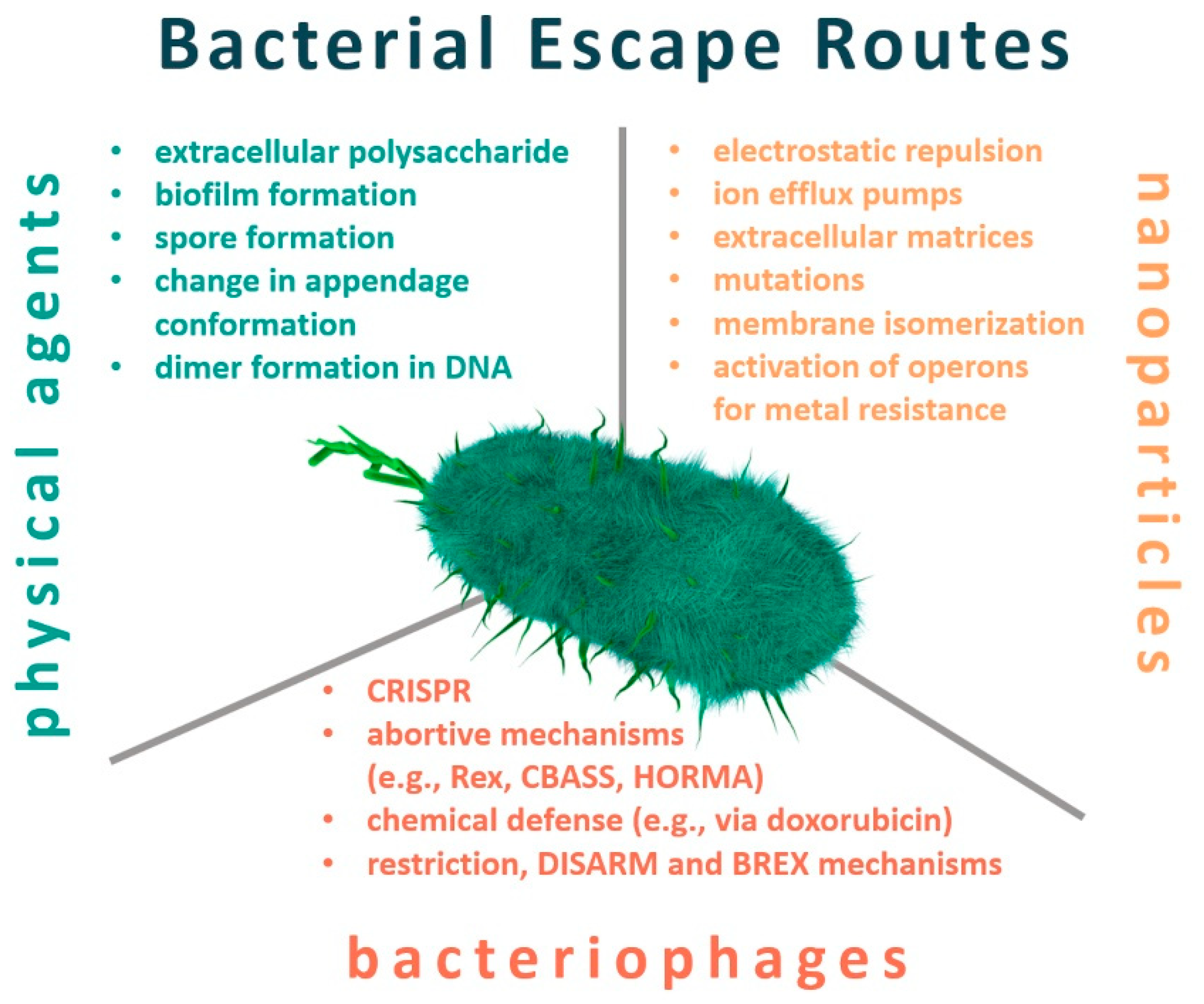
Antibiotics Free Full Text Resistance And Adaptation Of Bacteria To Non Antibiotic Antibacterial Agents Physical Stressors Nanoparticles And Bacteriophages Html
No comments for "Describe Two Ways in Which Antibiotic Resistance Can Become Widespread"
Post a Comment